Chuhai is a term that literally means “heading out to sea” and refers to the trends of Chinese brands entering foreign markets. This is a complex journey where each player forges its own path.
Tech giants stand out among the Chinese companies that have established operations in new countries. These conglomerates entered emerging markets such as Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Africa even before the term chuhai became common parlance at home. They have a deeper understanding of these markets and their industries than other startups that came onshore.
To unpack these developments for interested parties and entrepreneurs who are venturing abroad, 36Kr has started a new series titled “The global investment landscape of China’s tech giants” to illustrate some of the business opportunities that these players focus on overseas markets.
To kick off the series, we start by looking at Tencent’s investments in 23 companies in emerging markets. These firms are located in the four most popular chuhai destinations—Southeast Asia, India, Africa, and Latin America.
Tencent has three major investments in Latin America, two in Africa, 12 in India, and six in Southeast Asia. This entry will focus on Tencent’s businesses in Southeast Asia.
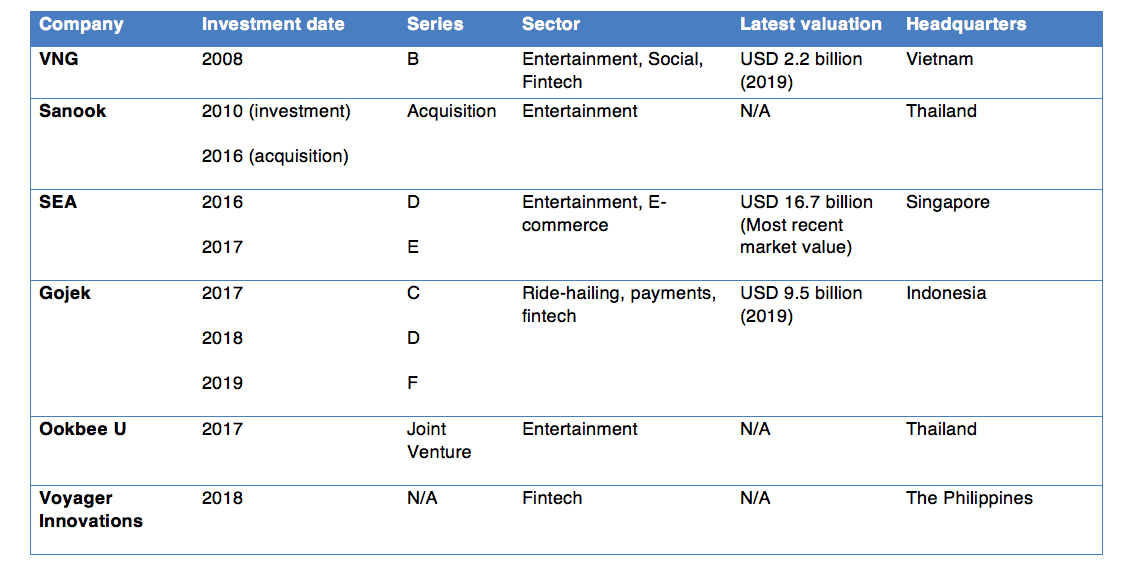
VNG
Founded in: 2004
Sectors: Entertainment, social media, and fintech
Overview of the company: Vietnam-based VNG started as a massively multiplayer online role-playing game (MMORPG) publisher. Tencent has held stakes in VNG for several years and currently owns 6.35% of the company’s voting shares. The firm first distributed the popular Sword Heroes Fate under the localized name Vo Lam Truyen Ky. The game was developed by Beijing-based software developer Kingsoft, who secured a strategic investment from Tencent in 2011.
Since then, many of VNG’s products have borne some semblance to the Chinese giant conglomerate. Among them, there is Zing, called the “Vietnamese QQ”; Zalo, a platform that resembles WeChat, and Zalo Pay, which echoes WeChat Pay. In 2017, VNG signed a memorandum of understanding to list its shares on the Nasdaq Stock Market, co-founder and chief executive officer Le Hong Minh said, without disclosing the timing or size of the expected IPO.
Competitors: WhatsApp and Sea Group
Sanook
Founded in: 1998
Sector: Entertainment
Overview of the company: Sanook began as a Thai-based web directory and developed into an all-inclusive platform including web portal Sanook.com, news application NoozUp, music-streaming platform Joox, and e-commerce site Sabuy. Tencent made a high-profile acquisition of Sanook in 2016, rebranding it as Tencent (Thailand) Company Limited, and currently plays a hands-on role in the management with seats on its board.
Today, the firm offers similar named applications such as music streaming service Joox by Tencent, one of the market leaders in Asia, the live-streaming platform Voov; and NoozUp, which resembles Tencent’s content aggregator Toutiao. Managing director of Tencent Thailand Co Krittee Manoleehagul said in late March of this year that his company has a large customer base, with 20-30 million users from Sanook, Joox, and other games.
Competitors: Spotify and TikTok
Sea

Founded in: 2009
Sectors: Entertainment, e-commerce
Overview of the company: Formerly known as Garena, Singapore-based Sea was the first tech company in Southeast Asia to be listed on the New York Stock Exchange. The company has two main streams of business—gaming platform Garena and e-commerce platform Shopee. As of the first quarter of 2019, Sea’s Free Fire—a mobile game inspired by PlayerUnknown’s Battlegrounds—has gained over 450 million users, making it the world’s second most downloaded game. Meanwhile, Shopee’s annual gross merchandise volume has been consistently above the USD 10 billion mark for the past three years. According to AppAnnie, Shopee was the most downloaded app in Southeast Asia and Taiwan in 2018.
Tencent has partnered with Sea to distribute its game titles in the Southeast Asia market. The platform is currently selling Tencent’s most popular games, including Arena of Valor, the international version of Chinese game Honour of Kings, and League of Legends.
Competitors: Lazada and Tokopedia
Gojek

Founded in: 2010
Sectors: Ride-hailing, payments, and finch
Overview of the company: Gojek started out as an Indonesian-headquartered motorbike-hailing platform, but has since developed its ambitions to become the first super app of Southeast Asia. Its business model resembles that of Chinese companies such as Didi, Meituan, and Alipay. Rooted in the largest market in Southeast Asia, Gojek is Indonesia’s first decacorn after its valuation hit USD 10 billion last April. The company has been expanding its reach through acquisitions and fundraising.
Tencent’s first investment in Gojek was in 2017, when it poured in USD 1.2 billion. Afterward, it led two rounds including Gojek’s USD 1.5 billion Series E in 2018 and a USD 920 million Series F (alongside JD.com, and Google). Tencent’s latest investment was in February this year whereby it co-led the USD 1 billion first close of Gojek’s Series F with Google, JD.com, Mitsubishi Corporation, and Provident Capital. Gojek today has a valuation close to USD 10 billion.
Competitor: Grab
Ookbee U
Founded in: 2017
Sector: Entertainment
Overview of the company: Thai-based Ookbee U (formally known as Ookbee) started out in 2012 as a content platform focusing on developing eBook stores across Southeast Asia, with more than 5 million customers in the region in countries such as Thailand, Vietnam, Philippines, and Malaysia. Most of the platform’s books are from renowned publishers or independent authors. The platform later partnered up with Tencent to form a joint venture called Ookbee U in 2017. Today, the platform offers user-generated content and has more than 10 million users. Its mobile app provides a range of content, from novels to comics, horoscope readings, quizzes, and music.
Competitors: Manga Toon and Wattpad
Voyager Innovations

Founded in: 2013
Sector: Fintech
Overview of the company: The Philippines’ Voyager Innovations company marked in November 2018 the largest funding round in the country, collecting USD 175 million, from PLDT, the country’s leading telecommunications and digital service provider, joined by global investment firm KKR, and Tencent.
Voyager is a prominent technology company in its home country, which aims to develop customer-centric emerging market platforms, especially in digital payments, digital finance, and marketing technologies. The company’s portfolio consists of various digital services, such as the digital wallet PayMaya, mobile-based remittance network Smart Padala, and the lending platform Lendr.
Competitor: Ant Financial-backed Mynt
Apart from Tencent, there are other tech giants that have invested heavily in Southeast Asia. One of them is Alibaba, and in our next entry of “The global investment landscape of China’s tech giants” series, we will explore this company’s investment in the SEA market.
This entry is based on a Chinese article originally published on 36Kr, KrAsia’s parent company. You can read the original article here.
36Kr is KrASIA’s parent company.
